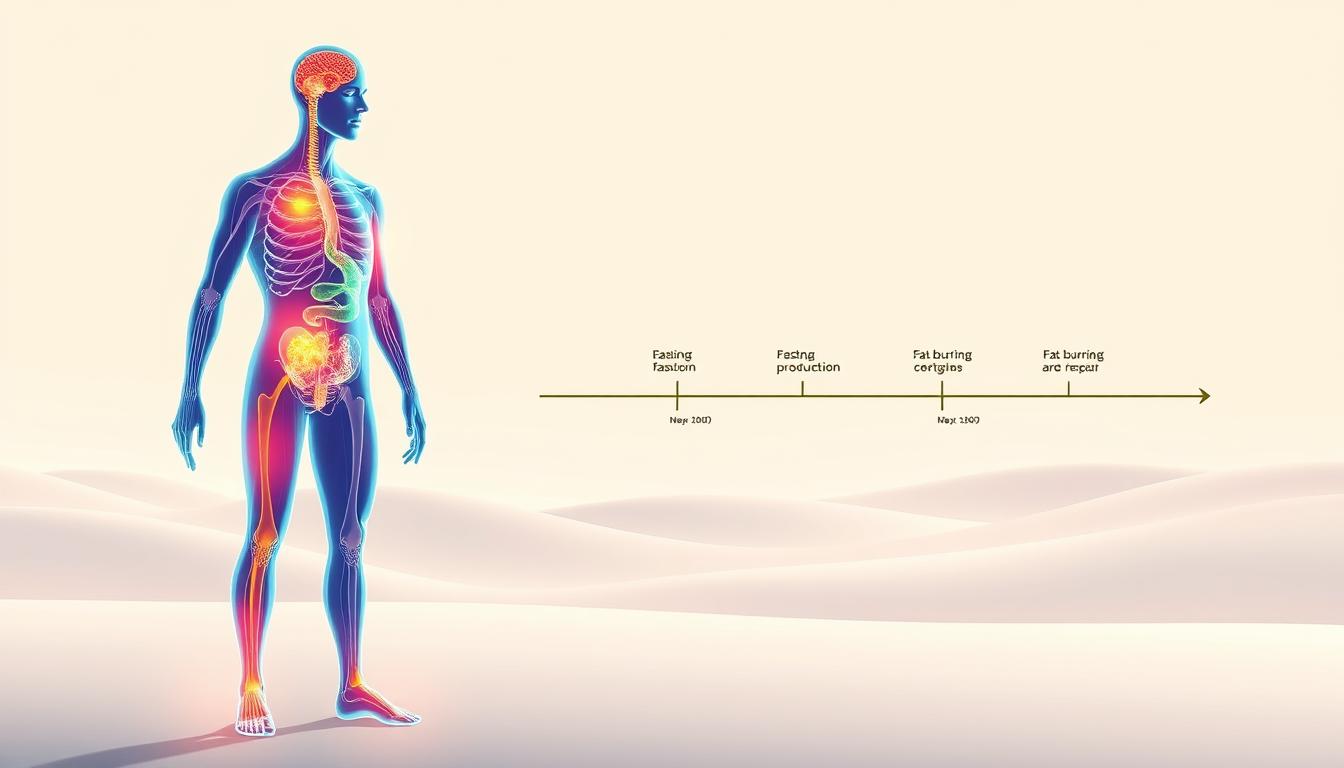
A growing body of research suggests that adopting an intermittent fasting regimen can have a significant impact on overall health, with many individuals experiencing improvements…
Best Workout Plan for Body Recomposition Beginners
Embarking on a body recomposition journey can be both exciting and intimidating, especially for those just starting out. Did you know that a well-structured workout…
How to Lose Fat and Gain Muscle at the Same Time
Achieving simultaneous fat loss and muscle gain is a highly sought-after yet challenging fitness goal. Research indicates that a well-designed training and nutrition plan can…
Delicious Plant-Based Protein Snacks for Weight Loss
A growing number of people are turning to vegan protein snacks as a convenient and healthy way to support their weight loss goals. With the…
Easy Vegan Meals for Lean Muscle Gain
A well-planned plant-based diet can be incredibly effective for building lean muscle. Did you know that some of the world’s top athletes thrive on a…